3.2.7.4. Conclusion
J. Ruzicka, M. Davis, M. Hatta and Ch. I. Measures © February 2024
While at the outset of this project it was already established that programmable Flow Injection can, by using LOV platform, accommodate a variety of reagent-based assays (Section 3.2.4.2.), the design of multipurpose analyzer was missing a key component, the multipurpose detector.
Because replacing PMT with more versatile CCD would be practical only if sensitivity of fluorescence monitoring with CCD and PMT was the same, preliminary experiments with fluorescent dye were done by using LOV platform (Section 3.2.7.1.) and software protocol (Section 3.2.5.2.) to carry out Single Standard solution calibration using 20 ppB fluorescein as sample. It was found that the thus obtained calibrations with PMT detector (A) and CCD detector are almost identical. This was achieved by maximizing intensity of illumination and integration time of CCD (Section 3.2.7.2. C, D), however it is likely that more sensitive CCD constructs will achieve the same result with shorter integration times.
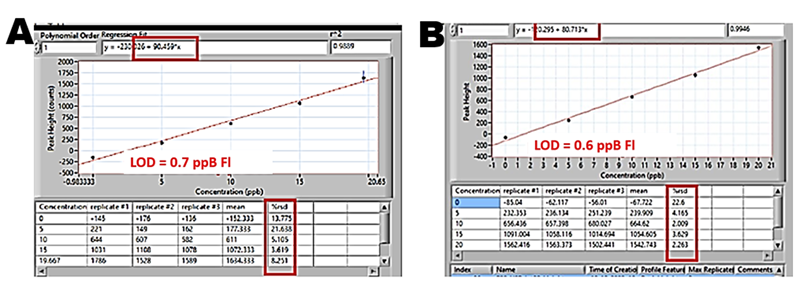
The limit of detection of fluorescein measured at 525 nm can be also used to compare sensitivity of the vintage USB4000-F used by us, with more sensitive spectrometers of present generation. The above comparison also suggests that use of CCD for measurement of fluorescein labeled reagents, widely used for analysis of biomolecules is feasible and actually preferrable, because different fluorescence labels emit at different wavelengths, and intensity of emitted light is influenced by pH, by presence of surfactants and by molecular interactions. (see Molecular Probes).
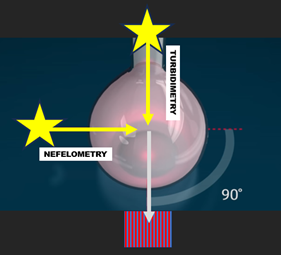
Scattering of radiation by suspended particles is used to measure their concentration by turbidity or by nefelometry. Turbidity like absorptiometry is less sensitive but yields a wider linear response. Both methods can use tungsten/halogen lamp for illumination although longer wavelength is said to be advantageous. Turbidity was used in cFI format for determination of sulfate precipitated by barium chloride reagent and for determination of chloride by silver chloride (Hansen Database). Turbidimetry and nefelometry are widely used for screening of water quality and of beverages. On an industrial scale turbidity is used to monitor water intake into desalinization plant.
Versatility, emphasized here, is only one of several advantages of the lab-on-valve based multipurpose instrument. In Air Segmented Continuous Flows Analyzers, sample travels through long, complex manifolds assembled from 2 mm I.D glass tubes, while in LOV manifold 0.8 mm I.D flow path is short (Section 3.2.6. Fig. C). This feature, combined with flow programming, saves reagents, and reduces volume of generated waste. All CFA instruments, as well as cFI, use peristaltic pumps, the Achilles Heel of continuous flow format. In contrast pFI -and the multipurpose instrument- use micro piston milliGAT pumps (Section 3.2.6.Fig.B) that generate well defined stabilized (within 0.3 r.s.d.) flowrates over several months, and therefore the instrument must be calibrated less frequently.
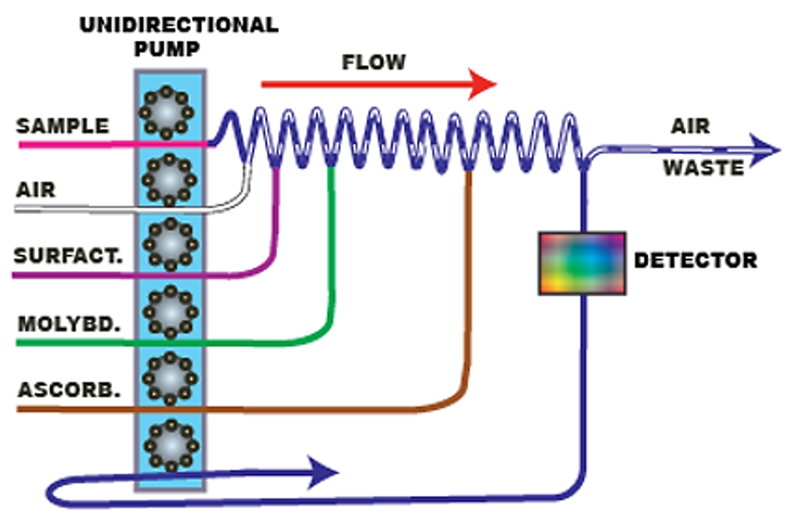 CFA manifold for determination of phosphate.
CFA manifold for determination of phosphate.