|
Engberg O, et al. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 132(40),
17536-40.
|
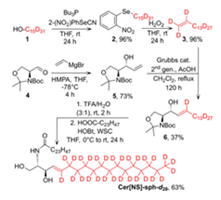
Synthesis of lipids, lipid analogs, labeled lipids, permeation enhancers, and dendrimers
We synthesize all major subclasses of human skin barrier lipids (including the ultralong acylceramides and omega-hydroxyceramides), including their analogs, and labeled variants (e.g., ceramides with deuterated sphingosine or acyl chains, fluorescent ceramides), to improve their analysis in the skin, understand their biophysical behavior, construct and improve in vitro models of the skin lipid barrier, and probe their potential to rescue lipid barrier in ichthyoses or atopic dermatitis. We have also synthesized numerous compounds that enhance cutaneous drug absorption (amphiphilic permeation enhancers based on amino acids, sugars, terpenes, and dendrimers).
|
|
 Vávrová K, et al. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2014, 134(3): 746-753. Vávrová K, et al. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2014, 134(3): 746-753.
|
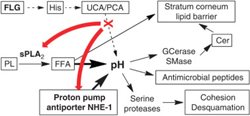
Analysis of skin barrier lipids
HPTLC is our method of choice for a fast overview of skin lipids (stratum corneum barrier lipids and their precursors); for a detailed ceramide analysis, we use LC/MS. We collaborate with several groups to reveal lipid changes in human/animal skin and 3D skin/epidermal constructs (filaggrin-deficient, PNPLA1-deficient, cancer, drugs, senescence, smoking...).
|
|
 Novackova A, et al. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2021, in press Novackova A, et al. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2021, in press
|
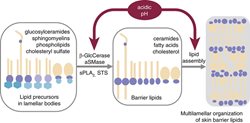
Biophysics and permeability of skin lipid models
Skin lipids are nothing like conventional phospholipid bilayers. These multilamellar extracellular lipid sheets contain ceramides, free fatty acids, and cholesterol. The acyl chains are tightly packed and rigid, and the dominant lamellar repeat distance is twice longer than the usual thickness of a bilayer. We aim at understanding the properties of the individual components of this mixture, their mutual interactions, their interactions with proteins, and the functional consequences (water loss and permeability to xenobiotics) of such lipid behavior.
|
|
 Kovacik, A. et al., Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17 (2), 145-155 Kovacik, A. et al., Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17 (2), 145-155
|
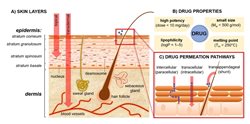
Transdermal and topical drug delivery
Drug administration via the skin has numerous advantages but is primarily limited by the remarkable barrier properties of the stratum corneum. We aim at enabling the delivery of a broader pool of drugs using permeation enhancers and micro- and nanosized formulations.
|
|
 Mauldin EA, et al Am. J. Pathol. 2018;188(6):1419-1429 Mauldin EA, et al Am. J. Pathol. 2018;188(6):1419-1429
|
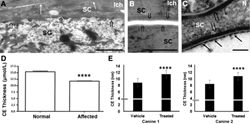
Lipids to rescue deficient barrier in skin diseases
The skin lipid barrier is perturbed in several skin diseases, such as atopic dermatitis and lipid synthetic autosomal recessive congenital ichthyoses. Replacement of the missing lipids has a strong potential for alleviating some disease symptoms and possibly preventing others without any significant side effects. To this end, we aim at identifying an effective, safe and inexpensive formulation for the treatment of such diseases.
|